





Published on Mar 09, 2021 by Anup Naick
Gate 2021 Chemical Engineering CH Syllabus : https://gate.iitb.ac.in : Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering (GATE) is a national examination, conducted jointly by Indian Institute of Science (IISc) Bangalore and seven Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) at Bombay, Delhi, Guwahati, Kanpur, Kharagpur, Madras and Roorkee on behalf of National Coordination Board (NCB)-GATE, Department of Higher Education, Ministry of Education (MoE), Government of India. GATE examination is a Computer Based Test (CBT).
GATE 2021 will be conducted for 27 Subjects (also referred to as “papers”).
GATE 2021 examination will be conducted over six days and twelve sessions on Friday 5th, Saturday 6th, Sunday 7th, Friday 12th, Saturday 13th and Sunday 14th of February 2021.
Linear Algebra: Matrix algebra, Systems of linear equations, Eigen values and eigenvectors.
Calculus: Functions of single variable, Limit, continuity and differentiability, Taylor series, Mean value theorems, Evaluation of definite and improper integrals, Partial derivatives, Total derivative, Maxima and minima, Gradient, Divergence and Curl, Vector identities, Directional derivatives, Line, Surface and Volume integrals, Stokes, Gauss and Green’s theorems.
Differential equations: First order equations (linear and nonlinear), Higher order linear differential equations with constant coefficients, Cauchy’s and Euler’s equations, Initial and boundary value problems, Laplace transforms, Solutions of one dimensional heat and wave equations and Laplace equation.
Complex variables: Complex number, polar form of complex number, triangle inequality.
Probability and Statistics: Definitions of probability and sampling theorems, Conditional probability, Mean, median, mode and standard deviation, Random variables, Poisson, Normal and Binomial distributions, Linear regression analysis.
Numerical Methods: Numerical solutions of linear and non-linear algebraic equations. Integration by trapezoidal and Simpson’s rule. Single and multi-step methods for numerical solution of differential equations.
Steady and unsteady state mass and energy balances including multiphase, multi-component, reacting and non-reacting systems. Use of tie components; recycle, bypass and purge calculations; Gibb’s phase rule and degree of freedom analysis.
First and Second laws of thermodynamics. Applications of first law to close and open systems. Second law and Entropy. Thermodynamic properties of pure substances: Equation of State and residual properties, properties of mixtures: partial molar properties, fugacity, excess properties and activity coefficients; phase equilibria: predicting VLE of systems; chemical reaction equilibrium.
Fluid statics, surface tension, Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids, transport properties, shell- balances including differential form of Bernoulli equation and energy balance, equation of continuity, equation of motion, equation of mechanical energy, Macroscopic friction factors, dimensional analysis and similitude, flow through pipeline systems, velocity profiles, flow meters, pumps and compressors, elementary boundary layer theory, flow past immersed bodies including packed and fluidized beds, Turbulent flow: fluctuating velocity, universal velocity profile and pressure drop.
Particle size and shape, particle size distribution, size reduction and classification of solid particles; free and hindered settling; centrifuge and cyclones; thickening and classification, filtration, agitation and mixing; conveying of solids.
Equation of energy, steady and unsteady heat conduction, convection and radiation, thermal boundary layer and heat transfer coefficients, boiling, condensation and evaporation; types of heat exchangers and evaporators and their process calculations; design of double pipe, shell and tube heat exchangers, and single and multiple effect evaporators.
Fick’s laws, molecular diffusion in fluids, mass transfer coefficients, film, penetration and surface renewal theories; momentum, heat and mass transfer analogies; stage-wise and continuous contacting and stage efficiencies; HTU & NTU concepts; design and operation of equipment for distillation, absorption, leaching, liquid-liquid extraction, drying, humidification, dehumidification and adsorption, membrane separations(micro-filtration, ultra-filtration, nano-filtration and reverse osmosis).
Theories of reaction rates; kinetics of homogeneous reactions, interpretation of kinetic data, single and multiple reactions in ideal reactors, kinetics of enzyme reactions (Michaelis-Menten and Monod models), non-ideal reactors; residence time distribution, single parameter model; non-isothermal reactors; kinetics of heterogeneous catalytic reactions; diffusion effects in catalysis; rate and performance equations for catalyst deactivation
Measurement of process variables; sensors and transducers; P&ID equipment symbols; process modeling and linearization, transfer functions and dynamic responses of various systems, systems with inverse response, process reaction curve, controller modes (P, PI, and PID); control valves; transducer dynamics; analysis of closed loop systems including stability, frequency response, controller tuning, cascade and feed forward control.
Principles of process economics and cost estimation including depreciation and total annualized cost, cost indices, rate of return, payback period, discounted cash flow, optimization in process design and sizing of chemical engineering equipments such as heat exchangers and multistage contactors.
Inorganic chemical industries (sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, chlor-alkali industry), fertilizers (Ammonia, Urea, SSP and TSP); natural products industries (Pulp and Paper, Sugar, Oil, and Fats); petroleum refining and petrochemicals; polymerization industries (polyethylene, polypropylene, PVC and polyester synthetic fibers).
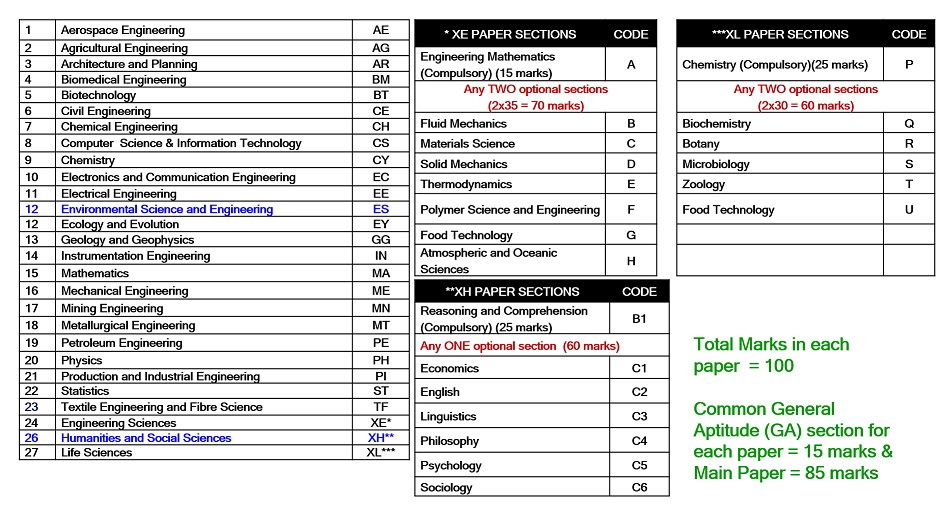
A candidate may appear either in ONE or TWO subject papers. For candidates who choose TWO papers, the combination must be from the approved list of combinations and subject to the availability of infrastructure and date.
Environmental Science and Engineering (ES) and Humanities and Social Sciences (XH) are two new papers introduced in GATE-2021.
Particulars |
Details |
Examination Mode |
Computer Based Test (CBT) |
Duration |
3 Hours |
Number of Subjects (Papers) |
27 |
Sections |
General Aptitude (GA) + Candidate’s Selected Subject |
Type of Questions |
|
Questions test these abilities |
|
Number of Questions |
10 (GA) + 55 (subject) = 65 Questions |
Distribution of Marks in all Papers EXCEPT papers AR, CY, EY, GG, MA, PH, XH and XL |
General Aptitude: 15 Marks + Engineering Mathematics: 13 Marks + Subject Questions: 72 Marks = Total: 100 Marks |
Distribution of Marks in papers AR, CY, EY, GG, MA, PH, XH and XL |
General Aptitude: 15 Marks + Subject Questions: 85 Marks = Total: 100 Marks |
Marking Scheme |
All of the questions will be of 1 mark or 2 marks |
Paper Code |
General Aptitude (GA) Marks |
Subject Marks |
Total Marks |
Total Time (Minutes) |
AE, AR, AG, BT, CE, CH, CS, CY, EC, EE, ES, EY, IN, MA, ME, MN, MT, PE, PH, PI, TF, ST and BM |
15 |
85 |
100 |
180 |
GG [Part A + Part B (Section 1 Geology OR Section 2 Geophysics)] |
15 |
25 + 60 |
100 |
180 |
XE (Section A + Any TWO Sections) |
15 |
15 + (2 x 35) |
100 |
180 |
XH (Section B1 + Any ONE Section) |
15 |
25 + (1 x 60) |
100 |
180 |
XL (Section P + Any TWO Sections) |
15 |
25 + (2 x 30) |
100 |
180 |
Candidates opting to appear in TWO subject papers must have a primary choice of paper, which will be their default choice and second choice of paper, which has to be chosen from the allowed combinations. Combinations other than the listed ones are NOT allowed. Under unforeseen circumstances, GATE 2021 committee has the rights to remove certain combinations at a later date. In such case, the fee paid towards the second paper will be refunded to the candidates. Also note that the examination centre for candidate to appear for the second paper may be different (but in same city) from that for the first paper due to the infrastructure and scheduling constraints. GATE committee is NOT liable for any legal obligations related to this issue.