





Published on Jan 09, 2026
Near Field Communication (NFC) Technology represents short range (practically up to 4 cm) wireless communication offering safe yet simple and intuitive communication between electronic devices that we use on a daily basis. Users of devices having NFC application in it can simply touch their devices to other similar elements having NFC application to communicate with them, making application and data usage easy and convenient. NFC can be called as the next generation of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) as technically its working principal is based on RFID however from application point of view it is similar to Bluetooth in some ways since it allows communication between two active devices.
NFC can be the future medium of contactless electronic payment as it inhibits eavesdropping on NFC - enabled transactions pertaining to its short range, however range can be extended by attackers using some range extension system. In this paper we briefly discussed the advantages, limits or challenges of NFC technology along with its applications which opens up exciting new usage scenarios for mobile devices.
Near Field Communication or NFC is a type of technology that soon will be a must for each gadget and is an integration of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology with mobile devices which allows them to communicate with each other by simply touching or bringing them very close to each other. RFID is used mainly for applications like indicating or identifying goods or persons without a line of sight while NFC on the other hand is used for more sophisticated and secure transactions like contactless access or payment. NFC is the outcome of joint work done by NXP Semiconductors (formerly Philips Semiconductors) and Sony Corporation [1]. Near field communication technology has already come in existence in many of the smart phones but still due to lack of awareness of people it is not in that much use. But with the growing popularity and demand for android applications, soon NFC will be found in every nook and corner of the world due to its compatibility with almost every existing technology in one way or the other. In this paper we will learn about different modes of communication and operation of NFC and discuss its advantages, limits or challenges posed by already existent technology, applications and future modifications required by the technology in a detailed way.
Near Field Communication (NFC) standards were first developed by the NFC forum, which was founded jointly by Nokia, Sony and Philips in the year 2004 with an aim to spread knowledge about NFC among people [2]. In December 2003, NFC was accredited with the standard ISO/IEC 18092 (NFC IP-1) which specifies the interface and set of rules to be followed for simple wireless communications between devices kept closely that does communication with transfer rates of 106, 212 and 424 kbps. In 2005, NFC also earned a further internationally accredited standard ISO/IEC 21481 which meant in the future it will soon become a known technology all over the world and will have various applications. According to the ISO standard, NFC is not encrypted which makes it compatible with previous RFID technologies
Using NFC, communication could take place between two active devices such as cell phones called active mode or even between a NFC device and a passive (or unpowered) ‘tag’ called passive mode [3]. In active mode, both the initiator and the target generate the RF signal on which the data is carried while in passive mode, RF signal is generated only by the initiator, and target communicates back to the initiator using a technique called load modulation (like using smart cards while travelling in metro) [4]. Also, battery less rewritable NFC tags are available that can store up to 4096 bytes of data. Thus nowadays mobiles are equipped with NFC reader and writer, which can be used to send data to and receive stored data from these tags.

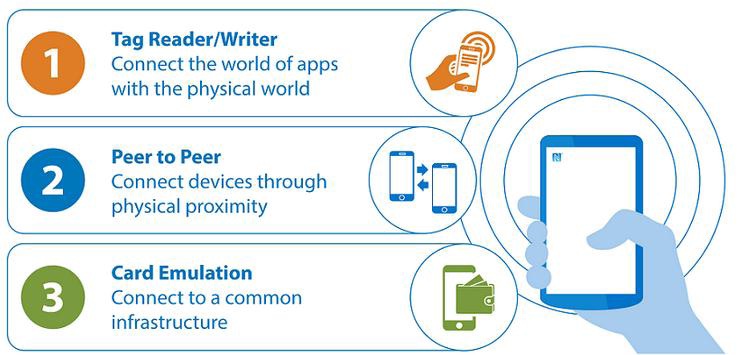
NFC has three operating modes; Peer-to-Peer, Reader/Writer, and Card Emulation. In order to standardize and spread the knowledge about NFC, NFC Forum [6] was formed which defined these operating modes because the communication way is different in each NFC mode and these differences effect the field of operation and usage areas accordingly
In card-emulation mode the data is copied from a NFC enabled mobile device to NFC-Reader. The most important feature of card emulation mode is elimination of physical objects and providing access control through user’s respective smart phones. Thus the most used mode of NFC too.
In reader/writer mode data is copied is from NFC tag to cell phone or vice-versa. This is a novel technology proposed by NFC and will become the user selling point of NFC in coming future.
In peer-to-peer mode data commutes between two NFC enabled active devices. But it is rarely used because of tough competition given by other wireless technologies like Bluetooth as it is more widely spread compared to NFC.
Mode of communication of the device whether active or passive, cannot be changed while the transaction is going on unless and until the target device vanishes i.e., removed or deactivated
NFC technology has several advantages over other wireless technology because it provides bidirectional communication for exchanging information i.e. both devices can send and receive data simultaneously unlike Bluetooth which promotes unidirectional communication [8].
NFC consumes less power in comparison of Bluetooth while working in active mode while more in case working in passive mode but Bluetooth has only active mode so NFC is more advantageous in this case [8].
Also less battery is utilized because NFC is built with built with lower transfer speeds of 106 kbps to 424 kbps [2].
Also there is no requirement of setting up a connection between two devices in action in case of NFC unlike that of Bluetooth. Thus NFC is easier to use especially in crowded places.
NFC can be used for handshaking i.e. setting up a connection between two devices without the need for any complex manual configurations. After connection setup within milliseconds other wireless technologies can come into play for work like data transfer etc.
Less probability of unknown connections setting up due to short range of communications like you don’t reset your phone just because you might have walked beside a smart tag. For that you need to knowingly make a connection.
Because of the simplicity NFC provides with along with simplifying other wireless technologies when integrated with them, it makes it easy enough for even the non-technical persons to use them.
Mobile devices can be used both as an information storage device or a NFC reader. They can read information from NFC tags which can further be manipulated and worked on accordingly. Also information like website account passwords or such type of confidential information can be stored thus it acts as a digital storage.
NFC can be used to build small devices as there will be no need for embedding any display unit in a device having NFC. The equipment can be touched by an NFC-enabled device and readings can be displayed.
Compatible with other contactless approaches, such as ISO 14443A, implemented in Philips’ Mifare and Inside Contactless’ PicoPass products; and ISO 14443B, the most popular standard, used with Sony’s FeliCa technology which too operate in the 13.56-MHz frequency range like that of NFC [9].
As the communication range for NFC is nearly 4 cm practically, thus when the devices are separated even a little distance apart, the communication ends which depicts in built security.
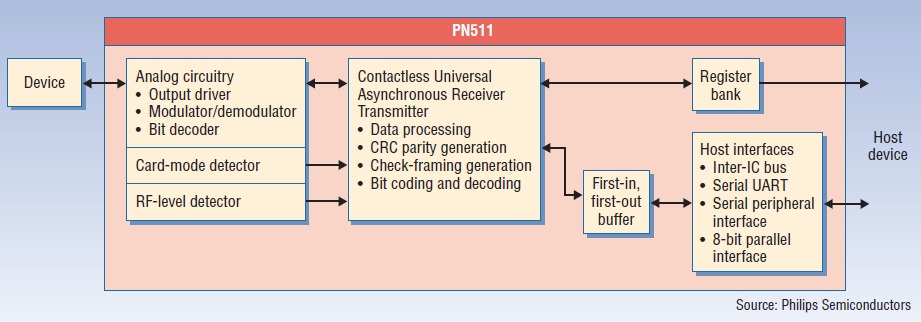
Components for NFC module can be integrated on one chip device as shown in Figure 3, saving space on the device which can be utilized for including other necessary functions and still keeping the size of the gadget small and handy.
With the use of NFC in the smart phones, they can be used in place of wallet, credit cards, debit cards etc. Cards with a direct physical contact interface are known as contact smart cards which receive power from the reader they are inserted in and exchange data with it using physical contacts while cards with a remote contactless interface are known as contactless smart cards which are waived from a very short distance so that electromagnetic wave from the reader will be used as the energy source, and wireless communication like NFC will be used for data exchange at the same time. SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) cards which are a must requirement in cell phones, in addition to authenticating users to the cellular network, contain a secure storage area, which provides necessary security conditions and performs data encryption and decryption. Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) and service providers such as banks use this area to provide value added services such as mobile financial services, e-government services, digital signature services, etc. to the users. Thus NFC is used for the electronic payment in which SIM card acts as a contactless smart card while the users smart phone acts as a mobile wallet

Contactless tickets, once introduced, will result in increase in speed and ease with which all consumers can use public transport like buses and access controlled environments like parking garages, transportation gates or get into events etc. Thus making travelling quite comfortable and fast [12]. Also provides flexibility of choosing sources and destination compared to present format and decreases wastage of resources like paper and time making it an eco friendly option along with providing better monitoring thus giving way for transparency of the system

NFC-enabled smart phones can be used as a room key in hotels making the check-in and check-out procedure free of standing in queues and waiting. Instead a person can directly enter their allotted rooms after making a booking and in return receiving a soft-key to their rooms
Near Field Communication has already begun to shape the future of electronic gadgets in people’s life. As the prices of chip manufacturing falls, the likelihood is that NFC-enabled mobile phones will become standard and their applications will become a part and parcel of life. According to a survey [17] it is found that NFC technology was preferred by people over other technologies including Bluetooth Beacons and QR codes. It is inferred that NFC technology works on the basis of RFID technology which uses magnetic field induction as a medium to establish communication between electronic devices placed closely and operating at 13.56 MHz as it is unlicensed frequency and can transmit data at a maximum rate of 424kbps [4]. NFC like any other technology has its own pros and cons.
When compared to other technologies however presently it is less popular but with the increasing android applications, soon it will become a need. In the present world where digital transaction are so common, there exist people who try to manipulate, disrupt or misuse the data that is transmitted and so users will no doubt initially be concerned about the security of their personal data that is stored on the NFC devices. Still besides this, it is a must application for smart phones and people need to be made aware about how it works.
[1] Kevin Curran, Amanda Millar, Conor Mc Garvey, (2012) “Near Field Communication”, International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE), Vol.2, No.3, pp. 371-382.
[2] Dr. Shyam Thangaraju, (2013) “Near Field Communication in Medical Devices”, White Paper, April 2013.
[3] Mohammad Umair Yaqub, Umair Ahmad Shaikh, (2012) “Near Field Communication, its Applications and Implementation in K.S.A”, report dated 13/02/ 2012, King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia.
[4] Anusha Rahul, Gokul Krishnan G, Unni Krishnan H and Sethuraman Rao, (2015) “NEAR FIELD COMMUNICATION (NFC) TECHNOLOGY: A SURVEY”, International Journal on Cybernetics & Informatics (IJCI), Vol. 4, No. 2, pp. 133-144.
| Are you interested in this topic.Then mail to us immediately to get the full report.
email :- contactv2@gmail.com |