





Published on Nov 30, 2023
Huge quantities of construction materials are required in developing countries due to continued infrastructural growth and inturn large quantities of construction wastes are generated every year. Wastes are also generated from various industries such as iron slag from steel industries, aluminium hydroxide from aluminium industries etc. The disposal of these wastes is a very serious problem because these wastes requires huge space for its disposal and pollutes the environment.Hence lot of research works need to be carried out to investigate to use these wastes as construction materials. Aluminium hydroxide and granite powder are two such industrial wastes generated in large quantities. Aluminium hydroxide is the waste generated during aluminium production.
From the literature it is observed that aluminium hydroxide is added to cement as stabilizer and to soil as flocculating agent. Aluminium hydroxide is not extremely sensitive to moisture content variations and is also used as fire retardant filler.
These are the desirable properties for additives used in soil stabilization. Granite powder is obtained from the granite slurry generated in granite processing industry.Granite powder has SiO2as the major component and small amount of calcium oxide which helps in the stabilization and hydration with cement. The grain size and specific gravity of granite powder is also suitable as an additive to cement.Since granite powder possess cementitious properties, it can be used as an additive with cement to develop soil cement stabilized masonry interlocking blocks. From the literature it was observed that Granite powder can be added in the range of 25-30% as an additive to soil and cement to get the optimum strength of soil stabilized block. Aluminium hydroxide can be added in the range of 4 - 10% as an additive to soil and cement to get the optimum strength of soil stabilized block. Hence this project intends to study the possibility of using aluminium hydroxide and granite powder as additives in the development of interlocking blocks.
Keywords : Granite powder, Aluminium hydroxide, soil stabilization
The main objectives of project are:
To arrive at optimum mix proportion of soil, cement, aluminum hydroxide and granite powder as additives in various proportions to get better strength.
To design the size and shape of the mould to obtain the interlocking blocks with suitable keys for better interlocking system.
To develop interlocking blocks using the pre-obtained optimum proportion.
To study the behaviour of interlocking blocks for compression, impact resistance, water absorption and sorptivity.
To study the compressive strength of masonry prism.
a. Material characterization:
Suitable tests have beenconducted on cement, soil, aluminium hydroxide and granite powder to characterize their properties.
The optimum proportion of the above materials are obtained for required compressive strengthof block based on different levels of combinations of additives. The required amount of water based on optimum moisture content (OMC) is added and thoroughly mixed to obtain a uniform consistent mixture. This mixture is used to produce the interlocking blocks using “Mardini press”- block making machine. From this the optimum mix proportion which gave better strength was considered for detailed studies of interlocking block.
The optimum mix proportion obtained by preliminary studies was used for the development of interlocking blocks. Interlocking block of specific size and shape with suitable interlocking keys is as shown in the figure.1 was cast and cured for 28 days. The masonry blocks have been studied for various properties such as
Compressive strength
Impact resistance
Water absorption
Sorptivity
The compressive strength of the masonry prisms made by these interlocking blocks is also to be studied. Suitable test to study the water ingress were conducted.
Suitable test to study the water ingress were conducted
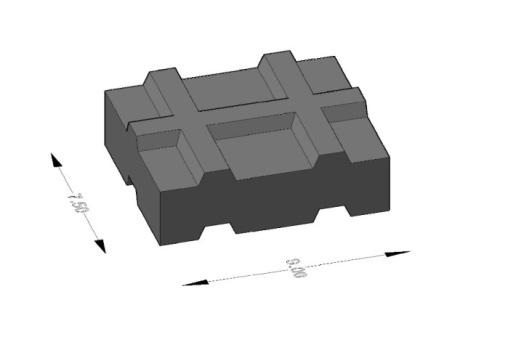
The blocks with 25-30% granite powder,3- 4% aluminium hydroxide and 10% cement showed higher strength.. It is found that with the increase in quantity of aluminium hydroxide the strength of blocks decreased. This decrease is possibly due to the increase in fineness of the mix. Hence M-sand was added to make it coarse.
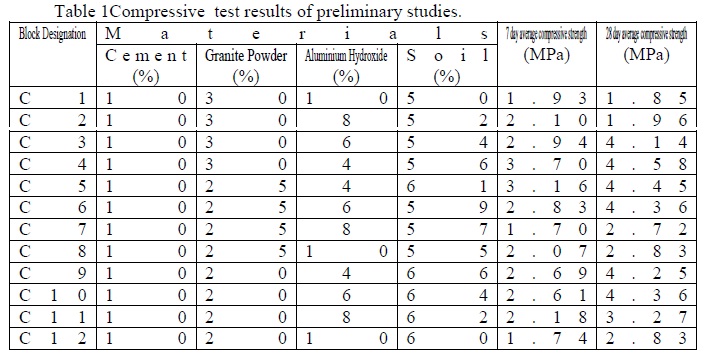
Table 2. Compressive strength of blocks of detailed study
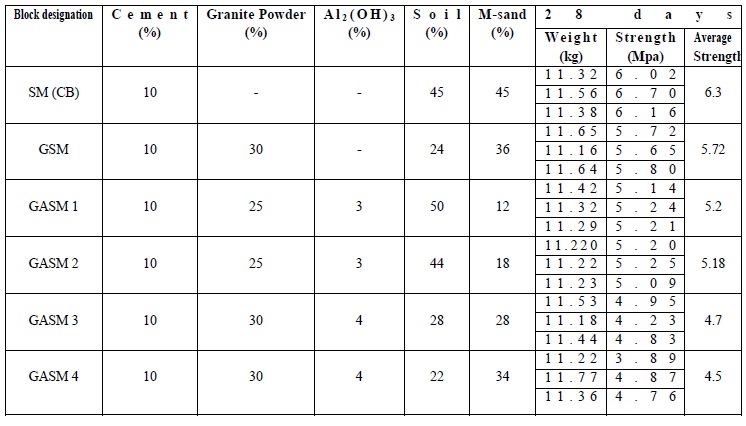
The compressive strength of control block was found to be 6.3 MPa.
The block GSM with 30% granite powder shows a compressive strength of 5.72 MPa.
It can be noted that with the addition of 30% of granite powder to Control Block (CB) a decrease in strength by 9.21 % can be seen. So the addition of granite powder to the soil stabilized block decreases its compressive strength.
The blocks GASM1 , GASM2 with 3% aluminium hydroxide and 25% granite powder shows a compressive strength of 5.2 MPa.
By the addition of 3% of aluminium hydroxide to the control Block and GSM the compressive strength decreases by 9.25%.
And by the addition of 4% of aluminium hydroxide to the Control Block and GSM the compressive strength decreases by 19.3%.
Hence block with only granite powder shows a decrease in compressive strength of 9.21%.
Hence block with both 25-30% granite powder and 3-4% aluminium hydroxide shows a decrease in compressive strength when compared to the control block
Hence by the addition of aluminium hydroxide and granite powder decreases the compressive strength of soil stabilized block.
According to IS 1077:1992,section 4.1 the blocks GASM1,GASM2,GSM and SM can be categorized as Class 5 and can be used for suitable construction purposes.
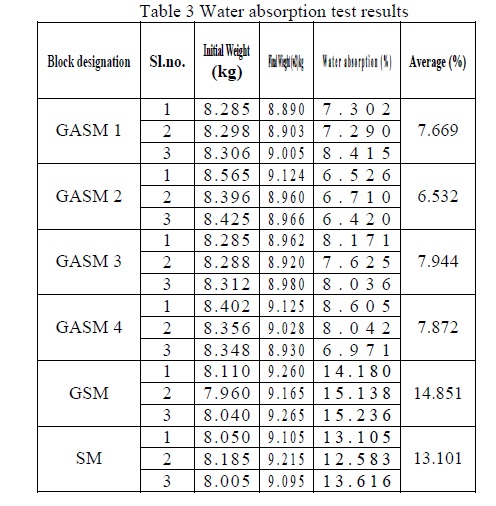
The blocks GASM 1 to GASM 4 in which aluminium hydroxide is added have water absorption value of 6-8%.
The blocks GSM and SM where alluminium hydroxide is not added have water absorption value of 13-14%.
Hence the addition of aluminium hydroxide decreases the water absorption capacity of the blocks.
As per IS 1077:1992,section 7.2,the bricks, when tested in accordance with the procedure laid down in IS 3495 (part 2):1992 after immersion in cold water for 24 hours,water absorption shall not be more than 20% by weight upto Class 12.5 and 15% by weight for higher classes.All blocks tested fall under Class 5 and have water absorption capacity within 15% satisfying the provision of the code IS 1077:1992,section 7.2. Hence these blocks can be used for construction purpose.
The sorptivity can be determined by the measurement of the capillary rise absorption rate on reasonably homogeneous material. Sorptivity (S) is a material property which characterizes the tendency of a porous material to absorb and transmit water by capillarity. It gains importance knowing the amount of water lost from the mortar.
I = S t 1/2=> S= I / t 1/2
The durability of the bricks can be improved by proper edge protection.
Lining at the joints can be provided to fill mortor paste after wall construction.
Other additives can be used which improves the strength of the interlocking blocks.
For the designed interlocking system different sizes of the bricks can be manufactured.
Concrete blocks can also be manufactured for the same interlocking system.
Reinforced masonry wall can be constructed by manufacturing suitable interlocking system with hollow opening at the centre.