





Published on Nov 30, 2023
Automatic Guided Vehicles (AGV) are designed to perform their operations without direct human guidance. They are used in a wide variety of industrial applications and can be laser, inertially or Cartesian-guided or GPS. An automatic guided vehicle system, (or AGVS) consists of one or more computer-controlled wheel based load carriers (normally battery-powered) that runs on the plant floor (or if outdoors on a paved area) without the need for an onboard operator or driver.
AGVs have defined paths or areas within which or over which they can navigate.
Navigation is achieved by any one of several means, including following a path defined by buried inductive wires, surface mounted magnetic or optical strips; or alternatively by way of inertial or laser guidance or GPS.
There are three main types of automatic guided vehicles, aside from custom or proprietary styles, unit load, forklift and tugger: Unit load automatic guided vehicles are powered, wheel based transport vehicles that carry a discrete load, such as an individual item (e.g. a large roll of paper, coil of steel or automobile engine) or items contained on a pallet or in a tote or similar temporary storage medium. AGVs operate under computer control without the need for human operators or drivers.
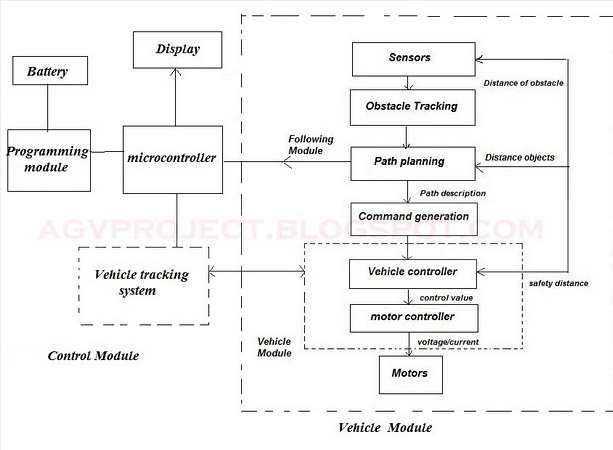
AGVs use one of two methods for guidance: Fixed path, where a physical guide path (e.g., wire, tape, paint) on the floor is used for guidance. Free-ranging AGVs have no physical guide path, thus easier to change vehicle path (in software), but absolute position estimates (from, e.g., lasers) are needed to correct dead-reckoning error. GPS tracking system can also be used for the purpose. Initially guided vehicles have an onboard gyroscope to determine and maintain heading.
Through onboard odometery, such as counting wheel rotations, the AGV calculates distances traveled. Many AGV systems using this combination of gyroscopic data and vehicle odometry go one step further: They achieve high precision in vehicle location by an under vehicle sensor detecting magnets or transponders embedded into the floor.
These automated guided vehicle systems have flexible and advanced navigation systems, and interface with elevators, doors and lifters. These AGV systems link Storage and production with light payloads to full pallet transport.
Pharmaceutical
Chemical
Manufacturing
Automotive
Paper and Print
Food and Beverage
Hospital
Warehousing.
Efficient automated material flow
24/7 material transport capability
Reduce dependence upon manual labor
Utilize existing right-of-ways
Minimize potential for injuries
Heavy weight lifting capability
Easily reconfigure changes in layout or function