





Published on Nov 30, 2023
The dawn of industrial revolution resulted in swift increase in the amount of industries, this rapid and uncensored industrialization resulted in, natural outcome of industries which in turn proportionally accelerated the industrial pollution to the environment on the other side. It is estimated that 15% of worldwide water is used for industrial purposes, while it is estimated that 3/4th by volume of waste water is generated only form of industrialsources. This current pattern of individual activity alters the natural flow of materials and introduces novel chemicals into the environment. The rates at which these effluents are discharged into the environment, especially water bodies, have been on the rise. Industrial pollution hurts the environment in range of ways and has negative impact on human life and health. The industrial waste constitutes, the major source, of various kinds of metal pollution in natural waters.
The tremendous increase in heavy metals in waste waters over past few decades has inevitably resulted in an increased flux of metallic substances in the aquatic environment.
The quality of water resources is deteriorating day by day, due to continuous discharge of municipal and industrial effluents to water systems. On the other hand, the demand for safe water is increasing continuously due to increase in population, living standards and industrialization. The Environmental Protection Act estimates that up to 50% of nation’s pollution is caused by industry alone, because of its size and scope, industrial pollution is a serious problem for the entire planet, especially in nations which are under rapid industrialization. The preservation and maintenance of natural water resources is now a burning issue. Water contaminated by heavy metals is more pronounced than other pollutants especially when heavy metals are exposed to natural ecosystems.
Contamination of water by toxic heavy metals through wastewater discharges from industrial activities is one of the major issuesof environmental concern. Various industrial activities like mining, electroplating, metal processing, textile, alloys, phosphate fertilizers, pigments, ceramics, glass, stabilizersand battery manufacturing industries are main sources of industrial heavy metal discharges. Also geological weathering, adds to this as a natural source for heavy metal contamination.
Keywords : Arecanut peel, Toxic metals, Synthetic waste water, Adsorption, Removal efficiency etc.
This project focuses on treatment of synthetic waste water containing heavy metals using arecanut peel. The main objectives are:
To study feasibility of using arecanut peel as an adsorbent in removal of heavy metals (Pb and Cd).
To study the effect of pH on removal efficiency.
To study the effect of time on removal efficiency.
To study the effect of dosage of adsorbent on removal efficiency.
To conduct isotherm studies and study interaction of adsorbent with adsorbate.
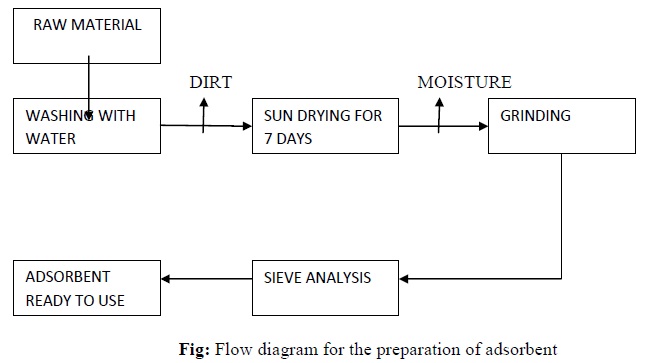
Preparation of adsorbent
The outer skin of arecanut peel was obtained after cutting into slivers. Therefore the peels were washed with pure water several times to remove dust and fines and air dried for 7 days. The air dried sample was later dried in oven at 70°C for 24hrs to prevent denaturing of cells. The oven dried sample was ground to fine powder using a grinding machine. It was sieved with a series of sieves of 90-460micronmeter meshes to obtain fine particles
Results of experimentation carried out under varied conditions of experimentation are tabulated and are represented by graphs and are documented in this chapter. Based on the results inferences have been drawn. The discussions are made in further sections and subsection emphasizing variables of experimentation on removal of toxic metals efficiency.
Experiments were carried out to evaluate the influence of contact time on removal efficiency. Three contact times viz. 15 and 30 min were considered for study. Based on the observations the following inferences have been drawn.
Linear and direct relationship between the cadmium and lead removal efficiency and contact time has been observed. Maximum removal efficiency for steady contact time of 30 min and minimum removal efficiency for steady contact time of 15min has been recorded. Same trends have been observed for all conditions of experimentation carried out.
pH viz,.4.5 and 9.0 were considered for the study to evaluate the effect of pH on the fluoride removal efficiency. Based on the observations, the following inferences were drawn.
pH has the indirect influence on the removal of cadmium and lead efficiency.
The removal efficiency for the pH4.5 is significantly more than that of 9.0 pHSame trend was continued in all the conditions of experimentation.
Adsorbent dosage viz, 1gm and 2.0gm were considered for the study to evaluate the effect of dosage on the cadmium and lead removal efficiency. Based on the observations, the following inferences were drawn.
Adsorbent dosage is direct influence on the toxic metal removal efficiency.
The removal efficiency for the adsorbent dosage of 2gm is significantly more than that of dosage at 1gm. Same trend was continued in all the conditions of experimentation.
Initial concentration viz, 5mg/L and 10mg/L were considered for the study to evaluate the effect of initial concentrations of cadmium and lead in removal efficiency. Based on the observations, the following inferences were drawn.
Initial concentration has the indirect influence on the toxic metal removal efficiency.
The removal efficiency for the 5mg/L is significantly more than that of 10mg/LSame trend was continued in all the conditions of experimentation.
The limitations listed above can be the subject matters for further study.
• Studies to access the removal of toxicity of other metals can be taken up for further study.
Based on the results of experimentation carried out under varied experimental conditions and the analysis of the same thereby following conclusions have been drawn.
It is concluded that the variables tried viz. adsorbent dosage, pHcontact time, initial concentration of chemical have good bearing on removal efficiency.
It is concluded that toxic metal removal efficiency is directly proportional to the adsorbent dosage and contact time.
It is concluded that toxic metal removal efficiency is inversely proportional to the pH.
The highest removal efficiency of Pb- 90% for optimum conditions of variables i.e. pH 4.5, initial concentration-10mg/L, adsorbent dosage-2gm,contact time-30 min have been recorded.
The highest removal efficiency of Cd- 91.10% for optimum conditions of variables i.e. pH 4.5, initial concentration-10mg/L, adsorbent dosage-2gm, contact time-30min have been recorded.