Step Up Transformer GCSE Physics Note
A step-up transformer is a key concept in GCSE Physics, especially when studying electricity and the National Grid. It’s a device that increases the voltage from the primary coil (input) to the secondary coil (output).
🔌 What is a Step-Up Transformer?
A step-up transformer is a device that increases the voltage from the primary coil (input) to the secondary coil (output). It’s used to transmit electricity more efficiently over long distances.
🧲 How Does It Work?
Transformers work on the principle of electromagnetic induction, and they only work with alternating current (AC).
🔄 Key Components:
-
Primary coil – connected to the power source.
-
Secondary coil – connected to the output.
-
Iron core – enhances the magnetic field between the coils.
💡 In a Step-Up Transformer:
-
The secondary coil has more turns of wire than the primary coil.
-
This increases the voltage output.
Also Read : Activate Your Wireless Service | Straight Talk
⚖️ Transformer Equation
VsVp=NsNp\frac{V_s}{V_p} = \frac{N_s}{N_p}
Where:
-
VsV_s = voltage in the secondary coil
-
VpV_p = voltage in the primary coil
-
NsN_s = number of turns in the secondary coil
-
NpN_p = number of turns in the primary coil
👉 In a step-up transformer:
Ns>NpsoVs>VpN_s > N_p \quad \text{so} \quad V_s > V_p
⚡ Why Use Step-Up Transformers?
In the National Grid, electricity is generated at around 25,000 volts but is stepped up to 400,000 volts for transmission. Why?
-
Higher voltage = lower current for the same power.
-
Lower current = less energy lost as heat (since power loss = I2RI^2 R).
Then, before electricity enters homes, a step-down transformer reduces the voltage back to safe levels (like 230V in the UK).
✅ Summary for GCSE
| Feature | Step-Up Transformer |
|---|---|
| Voltage | Increases |
| Current | Decreases |
| Coils | More turns on secondary |
| Use | Power transmission (e.g., National Grid) |
🧠 Multiple Choice Questions
1. What is the purpose of a step-up transformer in the National Grid?
A) To increase the current
B) To increase the voltage
C) To decrease the power
D) To store electrical energy
Answer: B) To increase the voltage
Explanation: Step-up transformers increase voltage to reduce energy loss during transmission.
2. If the primary coil has 200 turns and the secondary coil has 1,000 turns, the transformer is…
A) Step-up
B) Step-down
C) Reversible
D) Inefficient
Answer: A) Step-up
Explanation: The secondary coil has more turns, so it’s a step-up transformer.
🔢 Calculation Questions
3. A transformer has:
-
Primary voltage = 230 V
-
Primary turns = 100
-
Secondary turns = 1,000
What is the secondary voltage?
Solution:
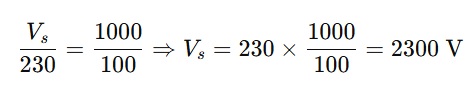
Answer: 2300 V
4. A transformer increases voltage from 25,000 V to 400,000 V. If the primary coil has 500 turns, how many turns are on the secondary coil?
Solution:
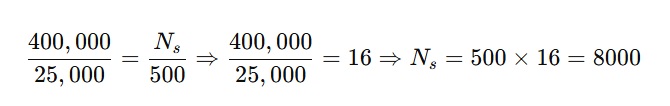
Answer: 8,000 turns
✍️ Short Answer Questions
5. Why is it important to reduce current in transmission cables?
Answer:
To reduce energy lost as heat. Power loss = I2RI^2 R, so lower current means less loss.
6. Explain why transformers only work with AC and not DC.
Answer:
Transformers rely on a changing magnetic field to induce voltage in the secondary coil. AC changes direction and creates this changing field. DC is constant and does not induce a changing magnetic field.