





Published on Nov 30, 2023
In recent years, the emergence of smart phones has changed the definition of mobile phones. Phone is no longer just a communication tool, but also an essential part of the people's communication and daily life. Various applications added unlimited fun for people's lives. It is certain that the future of the network will be the mobile terminal. Now the Android system in the electronics market is becoming more and more popular, especially in the Smartphone market. Because of the open source, some of the development tools are free, so there are plenty of applications generated. This greatly inspired the people to use the Android system. In addition, it provides a very convenient hardware platform for developers so that they can spend less effort to realize their ideas. This means Android can get further development.
Telecommunication, especially mobile phones have the potential to provide solution to the existing information asymmetry in various lagging sectors like agriculture. India’s agricultural sector suffers from low growth rates and low productivity. Issues in access to information are weak points at every stage of the agri-supply chain. For small farmer-based economy like India, access to information can possibly enable better incomes and productivity to the farmers.
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in agriculture is an emerging field focusing on the enhancement of agricultural and rural development in India. Using innovation is a key measure in the rural domain. The advancement of ICT can be utilized for providing accurate and timely relevant information and services to the farmers. We propose an android based mobile interface consisting several applications which include agro-based crop information, weather updates, loan informational updates, etc.
Keywords: — Android, Web Server, MySQL, PHP, HTTP
The availability and accessibility of information are the crucial points in taking the optimal decision at right time. Nowadays, advancement of ICT make possible to retrieve almost any information from the global repository (internet). The information in internet is primarily maintained in English. So, a large number of people are deprived from the benefit of internet due to technical and English language illiteracy. This scenario is very bad in developing country like India where nearly 76 % are English illiterate. Moreover, a large percentage of the English literate people are also unable to find their exact need form the large database of internet due to lack of proficient knowledge in English. Indian farmers belong to such type of people who are not much sound in both technical as well as in English.
So, they are unable to access required information on the farming life cycle, seed selection, pesticides, market price etc. from the internet. As a consequence, they are not capable to take optimal decisions at different stages of farming life cycle, which make huge impact on the farmer’s revenue. As a result suicide rate has been increased rapidly among the Indian farming community. According to the reports, those pathetic incidents are mainly happened due to the frustration that they are unable to pay their debts. These types of situations create huge impact on the agriculture sector.
Consequently, the focus of new generation is shifted from farming sector which will be threatening the near future in India. Our preliminary studies reveal that farmers require information at the right stage of the farming life cycle to take the right decisions. However, farmers are unable to get this information from internet due to English language and technical illiteracy. Recently, some web pages like –Wikipedia, Indian Railway web page, etc. provide facility of internet access in many users’ language other than English by supporting UTF-8 encoding3. However, it is observed that information is not so useful to the people who are having poor knowledge on internet and web browsing. Moreover, this type of attempt is meaningless for the illiterate people. A large number of people from the Indian farmer community are unable to read/write even their own mother tongue. So, it is obvious that text based interface, instead of supporting farmer’s own language, are not able to provide the required information.
1. An Iconic Interface integrated with a text to speech (TTS) engine to access the agricultural information from the internets' global repository for Indian farmer community.
2. Integrating a local repository with the interface to access urgent information without connecting to the internet.
3. Addition of applications which will be fulfilling the informational needs of the farmers.
4. All the above mentioned functions has to be carried out using an inexpensive mobile phone with an Android Operating System.
5. All the applications will be iconized for understanding of its function for an technically illiterate farmer.
6. Through our product we want to increase the curiosity among the farmer community with respect to technology which hopefully will lead to increase in the use of technology in the field of agriculture.
7. By introducing technology we also hope that this leads to encouragement of literacy among the remote villages of India.
8. And this product will also be helpful for the country’s youth who want to make their career in this field.
The methodology of our developed interface for the Indian farmer community is to access the agricultural information from the global internet repository and store them into local repository. We integrate the existing search engine (Google search engine) with our proposed interface.
1. The Android OS version 4.2.2 is chosen as the basic version which will be used to make the iconic interface.
2. A list of six applications was made after studying the required information which is needed by the farmers which are : Debt, Crop Availability, Farmers’ Market, NGO Help, Soil, Weather information.
3. The applications suitable to provide the information required by the Indian farmers are created using Eclipse version 4.2.2
4. Softwares like MySQL and Navicat were used to perform the required database operations.
5. There was a need for a web portal were the govt could decide upon the information which have to be sent to the KRISHI Interface.
6. Therefore for web portals java servlets were created using netbeans for three applications : Crop availability, Farmers’ Market and NGO Help.
7. The web portals were then connected to their respective applications by using local databases.
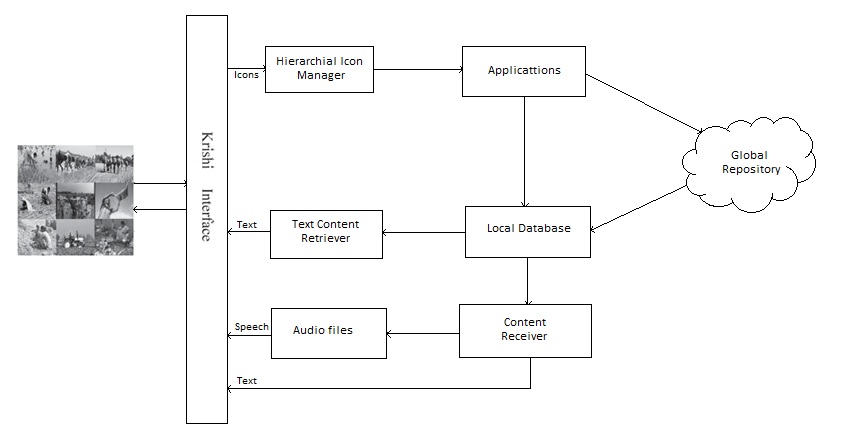
In Krishi interface user searches their agriculture related query through icons and gets the intended information in both textual and spoken form. Here we have developed six applications that satisfies the basic needs of a farmer, the applications are
The growing season is a term used for the period of time in a given year when the climate is prime for both indigenous and cultivated plants to experience the most growth. This period is observed in botanical, horticultural, and agricultural settings. The growing season of a given area can be affected by its relative distance from the equator, as well as elevation. Growing seasons are measured in two ways; the first being the number of consecutive frost-free days. This can be found by looking at the average last frost day of the spring for a given area, and then looking at the average first hard frost date in the fall or winter. The second way of measuring the growing season is by looking at the number of days in the year when the average temperature is above the point at which a crop will germinate. This method of measurement is affected by which crop you are intending on growing, so it varies considerably.
For example, wheat will germinate at temperatures above 40° F, while corn will only germinate at temperatures above 50° F. Karnataka agriculture is one of the most essential attribute of Karnataka economy. The topography of Karnataka such as the city's relief, soil, and climate immensely supports the agricultural activities in Karnataka. Agriculture in Karnataka is mainly done over 3 seasons: 1. Kharif (April to September) 2. Rabi (October to December) 3. Summer (January to March) The Kharif crops in Karnataka comprise millets, paddy (rice), maize, moong (pulses), groundnut, red chillies, cotton, soyabean, sugarcane, rice, and turmeric. It is also known as the Autumn harvest as it is cropped with the beginning of the first rains in the month of July. The major Rabi crops of Karnataka are wheat, barley, mustard, sesame, and peas. It is popularly known as the spring harvest in parts of Karnataka.
This application was created to help the farmers in understanding the growing season of the land. The application also has an iconic interface. Depending upon the cultivating season, the soil type etc conditions, and the application home page shows the images of the crops which will be most profitable to grow in the farm. When the image of any crop is clicked the information related to crop species, their ideal water requirements, and other important information is told. The information is written into the application which when clicked is converted into speech by using Google text to speech add-on.
Weather is defined as the state of the atmosphere with respect to wind, temperature, cloudiness, moisture and pressure. One of the most unique characteristics of the atmosphere is its water vapor content and the temperature which restores the water in three different properties or form such as solid, liquid and gas. Climate change and agriculture are interrelated processes, both of which take place on a global scale. Climate change affects agriculture in a number of ways, including through changes in average temperatures, rainfall, and climate extremes (e.g., heat waves); changes in pests and diseases; changes in atmospheric carbon dioxide and ground-level ozone concentrations; changes in the nutritional quality of some foods; and changes in sea level. Climate change is already affecting agriculture, with effects unevenly distributed across the world. Future climate change will likely negatively affect crop production in low latitude countries, while effects in northern latitudes may be positive or negative. Climate change will probably increase the risk of food insecurity for some vulnerable groups, such as the poor.
It is very important for us to foresee the next weather conditions in order for them to anticipate what is going to happen. By doing this, we will be able to know on how to provide an effective solution. This application helps the farmers in doing so. This will also of great help to farmers in order to prevent their loss and modify the farming practices which they make use of.
Global warming is the toughest environmental issues of today that all nations are combating. In this case, the farmers need to get educated on the types of farming techniques and strategies that must be used in order for them to give solution to any effects weather has something to do with the crops and livestock.
Indian agriculture is largely an unorganized sector. No systematic institutional and organizational planning is involved in cultivation, irrigation, harvesting etc.Institutional finances are not adequately available and minimum purchase price fixed by the government do not reach the poorest farmer. Government has implemented agricultural debt. waiver and debt. relief scheme in 2008 to benefit over 36 million farmers. Direct agricultural loan to stressed farmers under so called Kisan credit Card were also covered under this scheme. However, most of the subsidies and welfare schemes announced by the Central and State governments do not reach the poor farmers. On the contrary, only big land lords are benefited by those schemes.
The governments as well as the local NGOs are not able to reach the farmers. The NGOs provide various kinds of help but as there are very less farmers who know about such NGOs they rarely approach a NGO for help. This app helps the NGOs reach the common farmer. A farmer can get the details of the Ngo which can help them out regarding various problems whether they are related to family or the farm. This application helps them in placing a call to the Ngo and to share their problems.
A farmers' market is a physical retail market featuring foods sold directly by farmers to consumers. Farmers markets typically consist of booths, tables or stands, outdoors or indoors, where farmers sell fruits, vegetables, meats, and sometimes prepared foods and beverages. They are distinguished from public markets, which are generally housed in permanent structures, open year-round, and offer a variety of non-farmer/producer vendors, packaged foods and non-food products. Some farmers also prefer the simplicity, immediacy, transparency and independence of selling direct to consumers.
Farmers markets serve not only as a way for people to purchase locally grown produce but also as a chance for them to connect with others within their communities. Purchasing local goods is an experience that promotes a sense of place, important in making individuals feel tied to their communities. Managing markets properly will achieve the perfect social setting for people to meet and greet while they purchase their goods. Markets are anchored in community, connect people with each other and valued commodities, and create opportunities for business. Hence understanding the importance of farmers market, the application "Market" has been developed.
In this application whenever there is a farmers market organized by government or any other non government organization, the organization can register the event through the web portal. Once the event has been register it shows up on the home page of market application and also the farmer is sent a notification message. This way a farmer is made aware of the farmers market event happening in his region.
The basic requirements of farmers are seeds, pesticides, equipments and insecticides. Pesticides are substances meant for attracting, seducing, and then destroying any pest. They are a class of biocide. The most common use of pesticides is as plant protection products (also known as crop protection products), which in general protect plants from damaging influences such as weeds, fungi, or insects. In general, a pesticide is a chemical or biological agent (such as a virus, bacterium, antimicrobial, or disinfectant) that deters, incapacitates, kills, or otherwise discourages pests. Target pests can include insects, plant pathogens, weeds, molluscs, birds, mammals, fish, nematodes (roundworms), and microbes that destroy property, cause nuisance, or spread disease, or are disease vectors.
The good seed in a good field produces abundantly. Therefore it is very much required that the farmers must use pure, healthy seeds as per the minimum certification standards which have standard germination percentage. Infact the seeds is foundation of farming.The high good quality seeds are those which have genetic purity, physical purity, health standards, germiniability and moisture percentage in accordance with the minimum seed certification standards. Hence the farmer can increase approximately 20% production while he uses good high quality of seed. The farmer does make arrangements for many inputs but the seed is the chief input among other inputs. If the seed is of bad or low quality/sub standard then the labor and other expenses which the farmer does are in vain.
Modern farm machinery and equipment have now become so indispensable that farming won’t be the same without them. To be clear, farm machinery can be any equipment that help farmers till, cultivate, plant, harvest, and feed crops. They can be tractors, disks, plowers, wagons, planters, and more. One of the most significant contributions of farm machinery is time. With farm machinery to help farmers, farming time is significantly decreased. Now with farm machinery, more work can be done in just a fraction of the time that it took before. When farmers make use of a tractor and plow, it will only take him a couple of hours to cultivate an entire field that would take him a whole day if he used a horse-pulled plow. Farm machineries also help farmers and other large scale farm companies to save on capital and labor.
Farmers are often not aware of the shops where they can buy the seeds, pesticides, insecticides, and other items. This application gives the information of all the shops that sell items related to farming. Also this application will be helpful for farmers to compare the cost of the items in different shops. The home page is provided with icons which holds the image of seeds, pesticides, insecticides and equipments on clicking one of these icons the details of the shop that sell the item is displayed and the farmer is also provided with mobile number of the shop. Hence this application will be helpful for a farmer to choose a right shop to buy the goods.
India is an agrarian country with around 60% of its people depending directly or indirectly upon agriculture. Farmer suicides account for 11.2% of all suicides in India. Activists and scholars have offered a number of conflicting reasons for farmer suicides, one important reason is debt burdens. Around one-fifth of the total debt of the farmers is through non-institutional sources, of which commission agents are the most popular medium as they facilitate easy availability of credit at all times and for all purposes. Even though the farmers are being exploited by the non-institutional sources of credit, they turn towards them in times of need as they face a lot of problems in getting credit from institutional sources, including bank.
Therefore farmers are more likely to be cheated by the commission agents. One reason for this would be because they do not maintain a proper record of the monthly interest to be paid and the number of installments too be paid. In this application we try to help farmers in keeping account of all the debts that is being taken from the bank or any non institutional sources. The home page of the application contains an add user button which can be used to make record of a new loan that is to be taken. The home page also shows the listed view of all the debts that is taken from any financial organisation on clicking an item from the listed view a Detailed description will be displayed. An alarm is set for every one month to remind the farmer about the EMI payments.
At the current stage the Krishi-Bharati interface is limited to access the agricultural information in the context of Indian languages. However, it can be extended toward the agricultural context of any country in the world, which proves that the approach is generic. In future the speech to text can be added to the interface to provide additional benefits to the farmers. As of now the interface is providing information specific to the Karnataka local region. It has to be enhanced to cover the entire Indian subcontinent scenario. GPS Systems can also be integrated and various other applications can also be added into the interface.
The potential of information that affects the agricultural sector as a whole is very large. There is growing awareness about importance of information and its use among the farming community. Farmers must be able to get information delivered to them at a time and place of their choosing and it will be beneficial to farmer’s to realize productivity gains from the adoption of new farming practices and actions to mitigate crop losses. As mobile phone penetration continues to increase among the farming community and information services continue to adapt and proliferate, sufficient potential exists for a much deeper rural productivity impact in future, but achieving full productivity potential will depend on reducing other constraints which limit the use of information that farmers can obtain through their mobile phones.
Increased public and private investments will be necessary to bridge the critical infrastructural gaps. Policy changes may also be needed to encourage better access to high-quality inputs and credit for small farmers. Increased extension services and capacity-building efforts can complement information dissemination via mobile phones and associated services to accelerate the adoption of new techniques.
Mobile phones provide access to information which otherwise may not be available, especially to marginal and small farmers and farmers in the hilly region of the state. However, full realisation of potential benefits of mobile phones is limited by certain constraints which seem to apply more to marginal and small farmers rather than large farmers. These include infrastructure problems and availability of inputs, indicating that additional interventions are necessary to enhance agricultural productivity. Lastly, it is essential to note that use of ICTs may be motivated by needs other than “getting useful information”. In this case, mobile phones were mostly being used to fulfill social needs and their developmental use appears only incidental as indicated by high use for maintaining social networks and low usage to contact subject matter experts. However, successful cases indicate that mobile phones can be used for transforming agricultural practices. This would require appropriate and relevant content, enhanced trust in technology mediated communication and addressing of other critical factors simultaneously.
1. L. N. De Silva, J. S. Goonetillake, G. N. Wikramanayake, and A. Ginige, "Towards using ICT to enhance flow of information to aid farmer sustainability in Sri Lanka," in ACIS 2012: Location, location, location: Proceedings of the 23rd Australasian Conference on Information Systems, pp. 1-10. ACIS, 2012.
2. D. Samanta, S. Ghosh, S. Dey, S. Sarcar, M. K. Sharma, P. K. Saha, and S. Maiti, (2012, December). "Development of multimodal user interfaces to Internet for common people," in Intelligent Human Computer Interaction (IHCI), 2012 4th International Conference, pp. 1-8. IEEE, 2012
3. P. Madelaine, and M. Prabaker, "Tamil market: a spoken dialog system for rural india," In CHI'06 extended abstracts on Human factors in computing systems, pp. 1619-1624. ACM, 2006.