





Published on Jan 09, 2026
Engines are the major components of any automobile. A user of an automobile wants to get maximum power output from the engine, at the same time, not sacrificing fuel efficiency. The design of an engine is very important. One of the most important parts of engine design is the design of the combustion chamber. Different types of combustion chamber heads are being used at present.
One type of chamber head is the hemispherical head. The hemispherical head design enables the user to extract more power from the engine. The engines using hemispherical heads are known as HEMI engines.Modern HEMI engines are using various developments that have come up in the recent past. This has enabled these engines to provide the user with additional advantages apart from serving its major purpose, ie, supplying more power.
Engine is the basic component of any automobile. Combustion engines may be divided into two general classes - internal combustion engines and external combustion engines.In the external combustion engines, a working fluid is utilized to transfer some of the heat of combustion to that portion of the engine wherein this heat is transformed into mechanical energy.
The internal combustion engine inducts air from the atmosphere and the combustion of fuel and air occurs in or near that portion of the engine, which converts heat to mechanical energy. Internal combustion engines may be further classified into reciprocating engines and non-reciprocating engines. Internal combustion engines may also be divided as spark ignition engines and compression ignition engines.
Spark ignition engines may work in a two-stroke cycle or a four-stroke cycle. The four strokes involved are
1) Intake stroke
2) Compression stroke
3) Power stroke
4) Exhaust stroke
Any two strokes of a four-stroke engine will be coupled in a two-stroke engine.
The HEMI engine is a four stroke, spark ignition, reciprocating type, internal combustion engine.
The design of the combustion chamber for a spark ignition engine has an important influence on the engine performance and its knocking characteristics. The design involves the shape of the combustion chamber, the location of the spark plug, and the location of the inlet and exhaust valves. The important requirements of a spark ignition engine combustion chamber are to provide higher power output with minimum octane requirement, high thermal efficiency and smooth engine operation.
The HEMI engine was first developed in 1951 by the Chrysler Corporation. The advantage of HEMI engine over other engines of the time was that it produced more power. The reason for this was the efficiency of the combustion chamber.
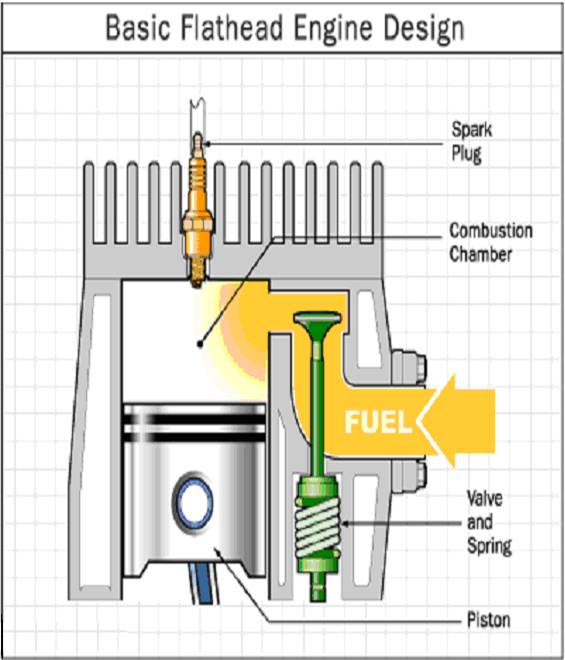
Most cars prior to the 1950’s used what was known as a flathead and many lawn-mower engines still use the flathead design today because it is less expensive to manufacture. In a flathead engine, the valves are in the block, rather then in the head and they open in a chamber beside the piston.
The head in a flathead engine (fig. 2.1) is extremely simple- it is a solid metal casting with a hole drilled in to accept the spark plug. The camshaft in the block pushes directly on the valve stems to open the valves, eliminating the need for push rods and rocker arms. Everything is simpler in the flathead engine. The problem with a flathead engine is its thermal efficiency.
In a HEMI engine (fig. 2.2), the top of the combustion chamber is hemispherical. The combustion area in the head is shaped like half of a sphere. An engine like this is said to have “hemispherical heads”. In a HEMI head, the spark plug is normally located at the top of the combustion chamber and the valves open on opposite sides of the combustion chamber
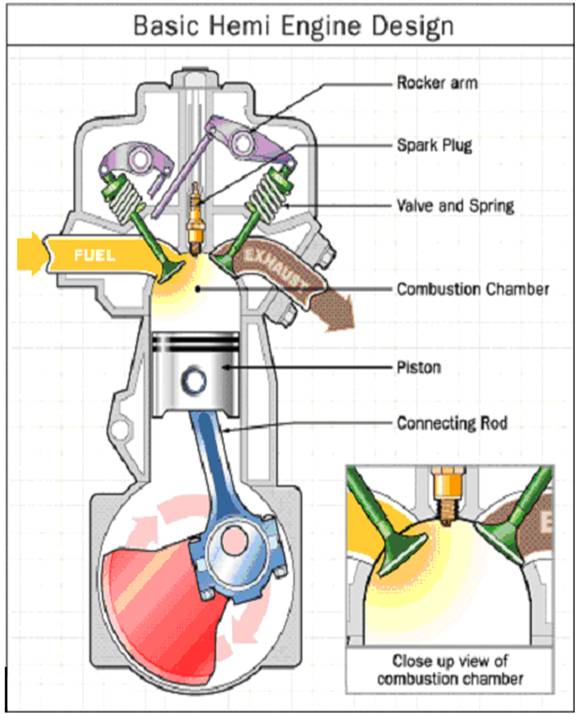
There are many different parts of an engine’s design that control or determine the amount of power you can extract from each combustion stroke.
You want to burn all the gas in the cylinder. If the design leaves any of the gas unburned, that is untapped energy.
You want the maximum cylinder pressure to occur when the crankshaft is at the right angle so that you can extract all of the energy from the pressure.
You want to waste as little as the engine’s energy as possible to suck air and fuel into the combustion chamber and pushing exhaust out.
You want to waste as little heat as possible to the head and the cylinder walls. Heat is one of the things creating pressure in the cylinder; so lost heat means lower peak pressures.
All these factors are satisfied in the HEMI engine because of its design. The last item in the list is one of the key advantages of the HEMI head versus the flat head engine. Surface area causes heat loss. Fuel that is near the head walls may be so cool that it does not burn efficiently. With a flat head, the amount of surface
area relative to volume of the combustion chamber is large. In a HEMI engine, surface area is much smaller than that in a flat head, and so less heat escapes and peak pressure can be higher.
Another factor with a HEMI head is the size of the valves. Since the valves are on the opposite sides of the head, there is more room for valves. The engine design that preceded the HEMI was a wedge shaped combustion chamber with the valves in line with each other. The in line arrangement limited valve size. In a HEMI engine, the valves can be large so that airflow through the engine is improved.
Thus, the HEMI engine delivers more power owing to its design. The design helps in attaining a high degree of turbulence (by inlet flow configuration or squish), high volumetric efficiency, improved anti-knock characteristics and compactness of combustion chamber.
Not all engines are using HEMI heads though they have the advantages mentioned earlier. This is mainly because of two reasons.
One thing that a hemispherical head will never have is four valves per cylinder. The valve angles would be so crazy that the head would be nearly impossible to design. Having two valves per cylinder is not an issue in drag racing or NASCAR because racing engines are limited to two valves per cylinder in these categories. But on the street, four slightly smaller valves let an engine breath easier than two larger valves. Modern engines use a pentroof design (fig. 3.1) to accommodate four valves.
Another reason most high performance engines no longer use a HEMI design is the desire to create a smaller combustion chamber. Small chambers further reduce the heat lost during combustion and also shorten the distance the flame front has to travel during combustion. The compact pentroof design is helpful here as well.
Today's HEMI is that in name only. Nowadays HEMI pentroof engines, due to the disadvantages mentioned earlier, are replacing the HEMI engines. It is found that the power delivered by these engines is greater than the power output from engines with I-head, H-head, L-head, T-head, etc.
These engines are being used more and more in modern cars. Though Chrysler is the major user of this type of engines, other motor companies are also beginning to use these engines with some variations because of the patent protection that is present for these engines.
HEMI engines also find a major application in cars being used for racing purposes.
| Are you interested in this topic.Then mail to us immediately to get the full report.
email :- contactv2@gmail.com |